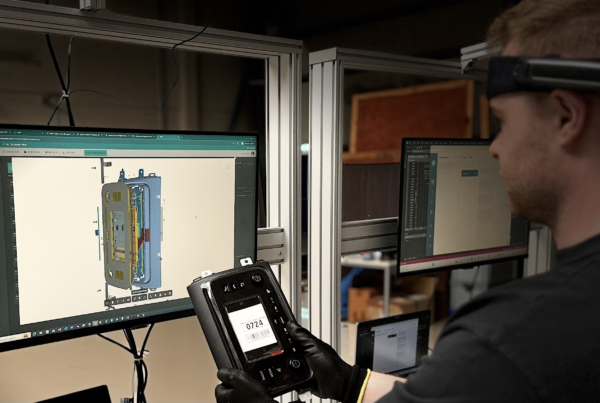
Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality: Shaping Industrial Future
We already learned about hands-free productivity in our previous article and now here we will learn about the technologies and their differences that allow frontline workers to go hands-free in industries. Augmented reality and virtual reality are the two main technologies that usually come up when talking about improving or replacing a real-life landscape with a virtual one.
These terms are not exactly novel technology. The first AR and VR gadget was created in the 1960s, which is a little-known fact. However, the technologies didn’t begin to mature into the use cases that we see today until a while ago when the internet became more widely available.

Both are largely dependent on and driven by advancements in internet connectivity and growing use by businesses and consumers. VR has been all the rage in the gaming world lately, while augmented reality is quietly making impacts in the manufacturing, logistics, and other industrial sectors. Though they both have a lot of promise for use in industry, gaming, marketing, and e-commerce are now the sectors where AR and VR are growing the fastest.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) joins digital and real-world elements. It adds virtual elements to the physical world just like layering computer-generated images or information on top of what you see in the real world. For example, when you use a mobile application such as Snapchat to view your avatar in your house or to add cool filters to your photos, all this is augmented reality.
What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality (VR) creates an overall immersive digital experience. When you put on a VR headset, it transports you to a 3D virtual world where you can interact with virtual environments and objects. It provides an experience where you feel as if you were there, and it is like stepping into a new virtual world completely.
The Difference Between Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Regardless of having similar concepts, virtual reality, and augmented reality reach two very different goals in entirely different ways. The technologies you use and the experience itself ultimately determine the differences as given below.
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
| Environment | Combines digital elements into the physical world setting | Fully immersive, completely virtual environment |
| User Control | Users maintain control and interaction with the physical world | Users are fully immersed, and the system controls them |
| Devices | Accessible through smartphones, AR glasses, or headsets | Requires a dedicated VR headset, often with controllers |
| Experience | Improves both physical and digital realities | Creates and improves an entirely fictional reality |
| Impact on Vision | Overlays digital content onto real-world views | Replaces the user’s vision with a virtual world |
| Current Usage | Growing adoption in retail, education, and industry | Significant advances in gaming, training, and simulations |
| Potential Impact | Changing real-world tasks with digital integration | Could redefine entertainment, education, and workspaces |
Few Examples of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality in the Real World
Many industries are already using these technologies. Among other sectors, healthcare, training, manufacturing, and logistics are also effectively using AR, VR and AI to gain benefits and optimize their processes.
For example, Dropslab Technologies specializes in providing AR and AI-powered solutions for industrial applications. Their user-friendly solutions are designed to improve training, maintenance, logistics, and construction. For example, their solutions combined with augmented reality devices enables remote assistance, and real-time data visualization which improves operational efficiency. Their solutions also allow frontline workers to view task steps and perform complex processes with ease in a safe environment. Similarly, they offer object detection and 3D models for assembly parts so there is no room left for errors in the production line, which improves the overall productivity.

Similarly, Nike used AR and VR in store to provide product information and allows virtual tours of their production line so customers can understand how and where the products are produced. While IKEA uses its AR-powered The Place App which assists shoppers in visualizing furniture in their homes and L’Oreal allows AR makeup try-on experiences for leading brands. Another example is the BMW and Jaguar which use VR for early vehicle design and engineering reviews before producing real-world cars and reduces costs on manufacturing.
Identically, healthcare professionals use virtual reality to get ready for the operating theaters and AR devices to identify tools, view operation steps, and much more while performing surgeries which decreases the possibility of errors.
The Future of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Many different reports predict that the AR and VR market will grow further in the upcoming years. As per Statista, the market is forecasted to increase at a yearly rate of 8.97% (CAGR 2024-2029) which will produce an approximated market volume of $62 billion (about $190 per person in the US) by 2029, currently standing at $40.4 billion (about $120 per person in the US) in 2024.
Currently, while virtual reality continues to grow within the gaming sector, augmented reality is largely being used in the industrial and manufacturing sectors. It drives on-site advancements, and digitalization, and is increasingly incorporated into Industry 4.0 processes to improve overall operational innovation and efficiency.