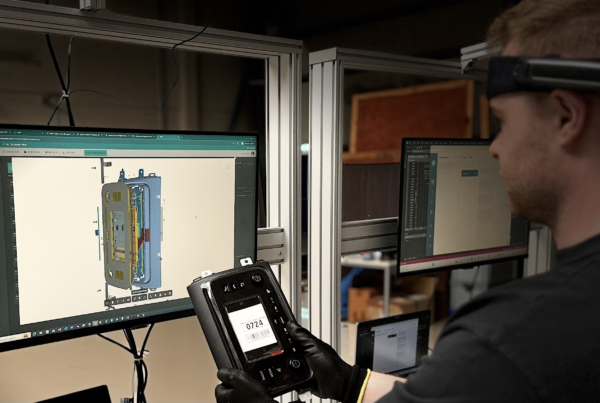
Digital Factory and Digital Factory Technologies
A digital factory is a manufacturing environment that integrates advanced digital technologies to streamline and optimise the production process. The concept combines elements of automation, data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and other digital innovations to create highly efficient, flexible, and smart manufacturing systems. Each of these digital factory technologies are important to improving efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability in industrial processes.
Here are 10 digital factory technologies that production line managers must know about. Let us find out how they impact the industry:
1. Cloud Connectivity
Cloud connectivity in smart manufacturing uses cloud computing for data storage, management, and processing. It offers scalability and flexibility. This technology enables centralised data storage and real-time processing. These are important for efficient task management. The impact of cloud connectivity on industry is notable as it decreases the infrastructure costs, improves collaborations and combines multiple processes and systems.
It uses advanced analytics and artificial intelligence to optimise tasks and adapts workflows to market demands. It guarantees data security, and privacy.
2. Big Data
Next in digital factory technologies we have big data. It includes processing, collecting and analysing huge and complex data sets from multiple sources like supply chains, machinery performances, and production rates. It helps with predicting maintenance needs, decreasing downtime, optimising supply chains, and improving decision-making.

This in results in increased product quality, production efficiency, and assists in continuous improvement and innovation, providing manufacturers with a competitive edge.
3. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
IIoT connects sensors, machines, and devices within the manufacturing environment, facilitating vast data exchange across the manufacturing process. In an industrial setting, IIoT improves real-time visibility and control, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and safety.
This digital factory technologies enables equipment monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process automation, reducing human error and boosting operational agility.
4. Digital Twins
Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems, updated in real-time with data from their physical counterparts for simulation, analysis, and optimization. Digital twins improve product design, and production efficiency. They help predict issues, support training, and provide a cost-effective testing and refining processes.
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Moving forward in digital factory technologies. let us now discuss AI. AI simulates human intelligence processes, including learning, reasoning, and self-correction, to automate complex tasks, enhance decision-making, and optimise production.
Artificial intelligence increases efficiency, reduces downtime, and enables predictive maintenance and quality control. It drives innovation by identifying patterns and trends, helping manufacturers stay competitive. Further in digital factory technologies, there is Machine Learning. Let us learn about it below.
6. Machine Learning (ML)
ML, a subset of AI, allows systems to learn from data and improve without explicit programming. It analyses data and makes informed decisions. Machine Learning also improves predictive maintenance, quality control, and real-time production adjustments, reducing waste and improving product quality. It optimises supply chain management and streamlines processes.
7. Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality overlays digital information onto the physical manufacturing environment, providing real-time guidance and support through devices like smart glasses and mobile apps. For example, Dropslab specialses in AR to reduce cost through real-time support.

Artificial intelligence improves precision and efficiency in complex tasks, reduces errors, and accelerates training. It provides contextual information for maintenance and troubleshooting, enhancing operational productivity.
8. Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics automate repetitive tasks with high precision and speed, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs. Automation increases productivity, enhances product quality, reduces waste, and improves safety by handling hazardous tasks.
9. Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
Additive manufacturing and 3D printing create objects by layering material from 3D models, enabling the production of complex shapes. This technology allows quick prototyping, decrease in material waste, and creation of lightweight, durable parts. It decentralises production and reduces environmental impact.
10. Blockchain
Blockchain is a decentralised ledger that securely records transactions, ensuring data integrity and transparency. Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency and traceability, supports quality assurance, compliance, and trust-building. It streamlines transactions, reduces costs, and increases efficiency.
These were the digital factory technologies. To know more about how you can integrate these in your workflow and production process, get in touch with the Dropslab team.
Conclusion
The integration of digital factory technologies is revolutionising manufacturing by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility. From cloud connectivity and big data analytics to AI, IIoT, and automation, each of these technologies uniquely contributes to the Digital Factory ecosystem, driving innovation and efficiency in smart manufacturing.
As industries continue to adopt to digital factory technologies, the shift toward smarter factories is inevitable, creating the path for a more competitive and sustainable future in manufacturing.
1. What is a digital factory?
A digital factory is a manufacturing environment operating with the help of advanced digital technologies like automation, IoT, AI, and cloud computing to streamline and optimize production processes. It provides efficient, flexible, and smart manufacturing systems.
2. How does cloud connectivity impact smart manufacturing?
Cloud connectivity offers centralisation, real-time processing, and advanced analytics that strengthen task management and collaboration. Further it lowers cost for infrastructure, easy adaptation to the demands of the market, and secure data protection.
3. What role does AI play in the digital factory ecosystem?
Artificial Intelligence performs complex tasks, makes better decisions, and maximizes production. It also allows for predictive maintenance, quality control, and innovation due to pattern and trend detection, which keeps manufacturers updated.
4. What is the significance of digital twins in manufacturing?
Digital twins are real-time virtual replicas that enable simulation, analysis, and optimization of physical systems. They improve product design, production efficiency, issue prediction, and reduce costs associated with testing and refining.
5. What advantages does blockchain offer for manufacturing?
Blockchain is a decentralised ledger that securely records transactions, ensuring data integrity and transparency. Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency and traceability. Evidently, blockchain is a core tool in contemporary manufacturing industries.