Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing
Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing may seem interchangeable, they represent distinct concepts, each crucial to the future of industrial operations. In this guide prepared by Dropslab, we shall understand the two terms, highlight the major differences, and also go through topics closely relevant to these.
Please Note- This is only a compact guide, not an academic paper.
What is a Smart Factory?
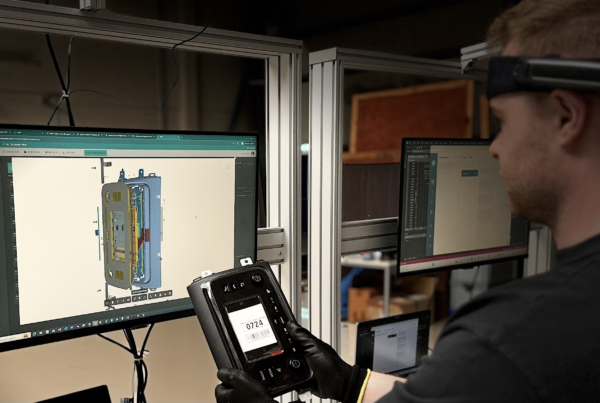
A smart factory is a facility that uses networked machinery and systems to collect data, sometimes in real-time, to enhance production processes from start to finish and support decision-making for executives, engineers, technicians, and line supervisors, among others. To do repairs before they break down, smart manufacturing equipment and machines also create data on how they are performing.
It is important to remember that manufacturers have long used automation and robotics. These establishments are not regarded as smart factories, though, until they employ fully integrated machinery and systems that merge the digital and physical domains. Smart industries frequently use 3D printing and sophisticated robots. The more general idea of smart manufacturing finds its practical application in smart factories. Moving forward in Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing, let us now see what smart manufacturing is.
What is Smart Manufacturing?
The idea behind smart manufacturing is to use digital and physical operations within factories and throughout the manufacturing production line in combination with technology. These procedures involve procurement of materials, transportation, manufacturing, and disposal. The two main goals of smart manufacturing are improving operational performance and responding quickly to fluctuations in supply and demand.
| Did you know
According to a survey conducted in 2023 by Sapio Research and Rockwell Automation, out of 1,350 manufacturers in 13 nations, around 97% of respondents stated that they intend to implement smart manufacturing technologies |
The Key Distinctions Between Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing
Even though Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing are usually used alternatively, these concepts are different, and here are five differences between the two.
| Aspect | Smart Manufacturing | Smart Factory |
| Scope and Concept | The main concept is to integrate modern technologies to improve physical and digital processes throughout the production line. | It includes real-world applications of smart manufacturing with integrated systems and advanced technologies like 3D printing and robotics. |
| Flexibility | Focuses on the complete production line to make it adaptable to market changes and customer demands. | Focuses on adjusting quickly to changes in demands or conditions within a factory. |
| Goal and Focus | Aims to improve operational performance and respond to changing supply and demand. | Concentrates on maximizing productivity while preventing downtime through predictive maintenance and tracking. |
| Application and Implementation | Applied throughout the entire manufacturing line, from material sourcing, logistics, and production to disposal. | A specific factory setting where smart manufacturing ideas are used to automate and connect processes. |
| Connection | Serves as the central concept that includes smart factories. | Represents the practical implementation of smart manufacturing principles within a facility. |
Above were some of the differences between Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing, let us now explore other related topics briefly.
How Do Smart Factories Work?
To gather and exchange data at every stage of the manufacturing process, smart factories use a network of sensors and software. This helps manufacturers increase production rates while also enhancing system maintenance and product quality. A robot may be programmed to provide fresh supplies just in time to prevent delays, for instance, if a bin on a manufacturing line at a factory has sensors installed that detect when the bin is running short on supplies. Furthermore, machines continuously provide data on their health, which helps to anticipate maintenance requirements and lower failure rates. In a smart factory, networked machinery also identifies material issues before faults occur.
Top 5 Benefits of a Smart Factory
Grand View Research projects that the global market for smart manufacturing technology, which includes sales of sophisticated software such as Dropslab Core and Dropslab Sense, robotics, sensors, and other digital assets, will reach US$787.54 billion by 2030 from US$254.24 billion in 2022. Below are the reasons why industries are investing in this technology:
1. Lower costs
A Smart factory reduces staff, errors, product defects, and lean waste. At the same time, it increases the machine’s life through predictive maintenance.
2. Data-driven decisions and Faster
Data from sensors helps improve decision-making at every stage of manufacturing and production lines.

3. Increase productivity
Automation reduces redundancies, eliminates waste, decreases downtime, and optimizes inventory management.
4. Fewer people required
Automated processes allow manufacturers to handle more work with fewer employees, addressing future labor shortages that usually come with unexpected sick leaves, etc.
5. Eliminate environmental effects
Intelligent technologies track sustainable materials and lower carbon footprints.
How to Get Smart and Transform Your Manufacturing Operations?
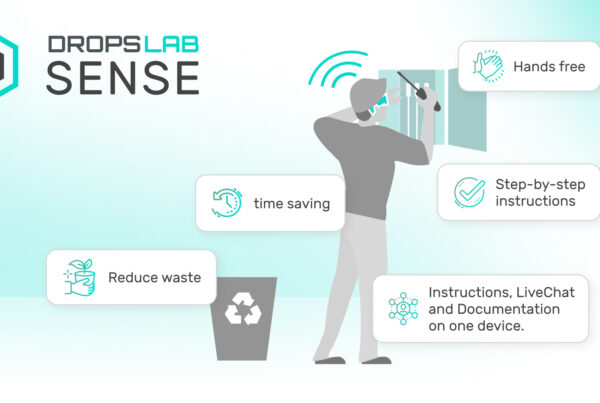
The solution is simple, use Dropslab’s solutions which include Dropslab Core and Dropslab Sense. These user-friendly tools provide all the benefits associated with the smart factory. You can schedule your daily tasks, stay connected with your team, have remote assistance, and much more with these products. Your workers do not have to go through traditional manuals to find a solution, they can simply look at the visualized workflows and learn the processes step by step.
Additionally, with real-time data and hands-free operation, Dropslab Core and Dropslab Sense help reduce errors, minimize downtime, and ensure efficient task execution. These solutions not only enhance productivity but also promote a safer and more collaborative working environment.
Conclusion
Even though the concept of a smart factory and smart manufacturing are closely related, they have different roles in the modern industry. One focuses on integrating the digital and physical processes throughout the entire production line while the other provides the application of these processes within a factory. Dropslab Technologies offers practical tools like Dropslab Core and Dropslab Sense to help companies fully shift to the smart factory so they can improve their production line and reduce extra costs.
FAQs
Below are some of the frequently asked questions for Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing. If you have any other questions, feel free to contact Dropslab.
What is the difference between Smart Manufacturing and Smart Factory?
Smart Manufacturing is the concept of integrating all forms of digital and physical processes to enhance operations and respond dynamically to supply chain dynamics. On the other hand, Smart Factory would represent the actual implementation of those concepts within a facility using technologies such as robots and sensors.
2. How does a Smart Factory improve operational efficiency?
A Smart Factory uses networked sensors, advanced robotics, and analytics to help optimize processes, minimize downtime through predictive maintenance, and eliminate waste. That is good for faster decision-making, lower costs, and higher productivity.
3. What are the key technologies of a Smart Factory?
Smart Factories apply technologies that include 3D printing, IoT sensors, robotics, cloud computing, AI-driven analytics, and platforms like Dropslab Core and Dropslab Sense to real-time monitoring and streamlined workflows.
4. Is a smart manufacturing system applicable for small and medium-sized enterprises?
Yes, SMEs can adopt Smart Manufacturing by starting with scalable solutions such as Dropslab Core and Dropslab Sense, which allow them to digitize their operations and gradually implement advanced technologies based on their needs and budgets.
5. How can Dropslab solutions help in transitioning to a Smart Factory?
Dropslab Core and Dropslab Sense can be applied with real-time tracking of data, hands-free operation, and step-by-step visualized workflows in the workflow. These tools make the transition towards a Smart Factory easier, minimizing downtime, reducing errors, and providing collaborative and sustainable manufacturing processes.