Repair and Maintenance
In every industry, the ultimate goal of a maintenance department is clear-to keep machinery and assets running smoothly. Failing to properly manage repair and maintenance, often leads to faster equipment wear, costly repairs, and unplanned downtime. In this article, we will take a closer look at the key differences between repair and maintenance, highlighting why understanding repair and maintenance are crucial for efficient operations.
Please Note- This article is not an academic piece on repair and maintenance. We suggest not to cite it as a source, academically.
The Cost of Unplanned Downtime in Manufacturing
Unplanned downtime is one of the largest causes of lost productivity in industries, leading to delayed projects, customer dissatisfaction, and substantial financial losses. According to recent reports, industrial manufacturers lose around $50 billion each year due to downtime caused by unaddressed repairs and poor maintenance planning.
What’s the Difference Between Repair and Maintenance?
The terms “repair” and “maintenance” are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings, especially when managing complex machinery and assets. Understanding the difference can help organizations optimize their processes and reduce downtime.
What Are Repairs?
Repairs are actions taken to restore an asset that has failed, bringing it back to its original functionality. Repairs are typically reactive, occurring only after an asset has malfunctioned or broken down.
Two types of failures require repairs:
1. Complete Failure
This type of failure leaves an asset completely unusable until repaired. For instance, a pump failure in a manufacturing plant will render the entire system inoperative until it is repaired.
2. Partial Failure
In this case, the asset continues to function, but with reduced performance or safety. For example, an air conditioning unit that is still working but blowing warm air due to a faulty compressor requires repair to restore full functionality.
Repairs can be costly, especially if the failure leads to significant downtime. Asset failures are often triggered by various factors such as aging equipment, mechanical failure, or operator error. While some failures are unavoidable, many can be prevented with effective maintenance.
What Is Maintenance?
Maintenance, in contrast to repair, refers to activities aimed at keeping assets in good working condition and preventing failures before they occur. Maintenance is proactive and aims to preserve the functionality, safety, and performance of assets over their lifespan. There are several types of maintenance, including:
1. Preventive Maintenance (PM)
Routine tasks performed on equipment to ensure it continues to function without issues. This might include regular inspections, lubrication, and minor component replacements.
2. Predictive Maintenance (PdM)
Uses data-driven insights and condition-monitoring tools to predict when an asset is likely to fail, allowing for repairs to be made before an actual failure occurs.
3. Corrective Maintenance
Performed after a fault is detected but before the asset becomes completely inoperative, aiming to correct the problem before it causes a complete failure.
4. Reliability-Centered Maintenance
A strategy used to optimize the performance of an asset by balancing reliability with the cost of maintaining it.
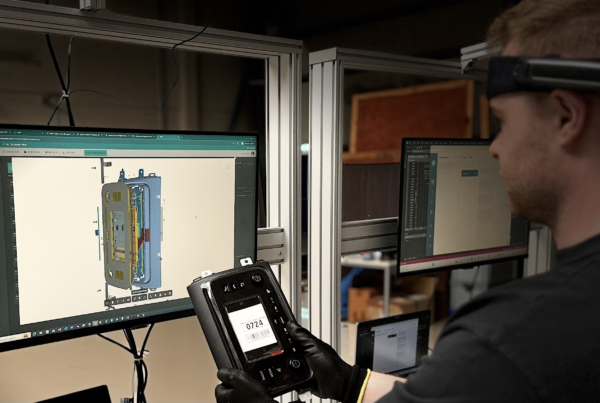
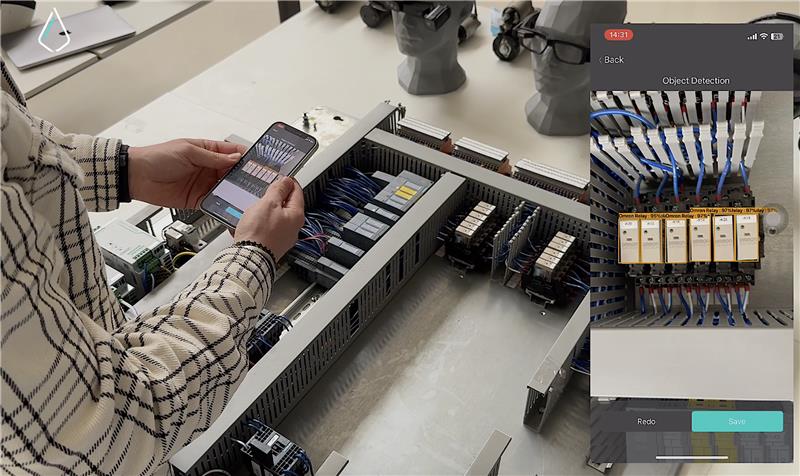
Incorporating maintenance into operations can significantly reduce the need for expensive repairs by identifying issues before they cause critical failures. Solutions like those offered by Dropslab Technologies help simplify these maintenance processes, providing real-time data to aid in decision-making and reducing overall downtime.
The Difference Between Repair and Maintenance: Why It Matters
While both repair and maintenance are essential for keeping assets running efficiently, the primary difference between repair and maintenance lies in the approach:
- Timing: Repairs are done after a failure occurs, while maintenance activities aim to prevent failure before it happens.
- Purpose: Repairs restore functionality, while maintenance preserves it.
- Cost: Repairs tend to be more expensive, especially if they involve emergency work, whereas maintenance is often more cost-effective in the long term.
By focusing on proactive maintenance, companies can extend the life of their assets and minimize the occurrence of costly repairs. Let us learn further about repair and maintenance, in the section below.
Simplify Preventive Maintenance with Dropslab
While repairs are inevitable, proactive maintenance can minimize them significantly. Industry experts recommend dedicating most of your resources to preventive maintenance to reduce unplanned repairs and downtime. Dropslab Technologies’ suite of tools, including Dropslab Sense and Dropslab Core, simplifies maintenance tasks with AI and AR. These solutions automate workflow management, assist in real-time diagnostics, track asset performance, and optimize maintenance schedules. With Dropslab, you gain more control over your operations, leading to better productivity and reduced costs.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between repair and maintenance is key to efficient asset management. Repairs address unforeseen failures, while maintenance prevents these issues. Focusing on proactive maintenance reduces downtime and extends asset life. Tools from Dropslab Technologies, like AR and AI, enhance preventive maintenance and expedite repairs. By integrating advanced technology into repair and maintenance, businesses can improve productivity and lower operational costs.
FAQs
Below are some of the commonly asked questions for repair and maintenance, if you have a question not mentioned below, feel free to reach out to our team.
1. Why is preventive maintenance so important?
Preventive maintenance is crucial because it reduces unplanned downtime, increases asset lifespan, and lowers the risk of costly emergency repairs. It helps organizations stay ahead of potential issues and maintain smooth operations.
2. How can technology assist in the repair process?
Technology, like AR-powered solutions from Dropslab Technologies, can significantly enhance repair processes by providing real-time diagnostics and guided instructions to technicians, which helps to reduce errors and speed up repair times.
3. Can maintenance fully prevent repairs?
While maintenance greatly reduces the frequency of repairs, some level of repair is inevitable, especially as equipment ages or faces unpredictable issues. However, a strong maintenance program can minimize these occurrences.
4. What role does data play in predictive maintenance?
Data is essential in predictive maintenance as it allows for the early detection of wear and tear, making it possible to address issues before they cause significant damage or downtime. Tools like Dropslab’s workflow management platform provide insights to help plan interventions before they become critical.