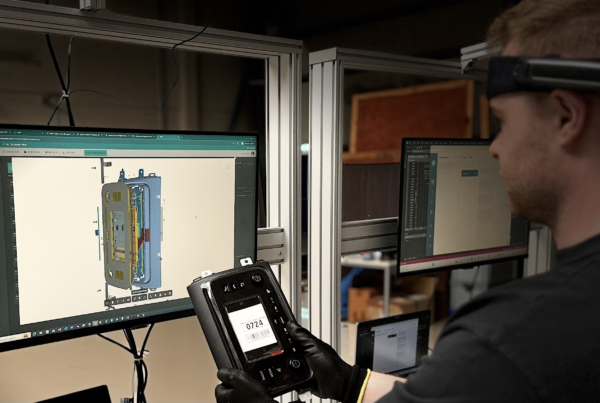
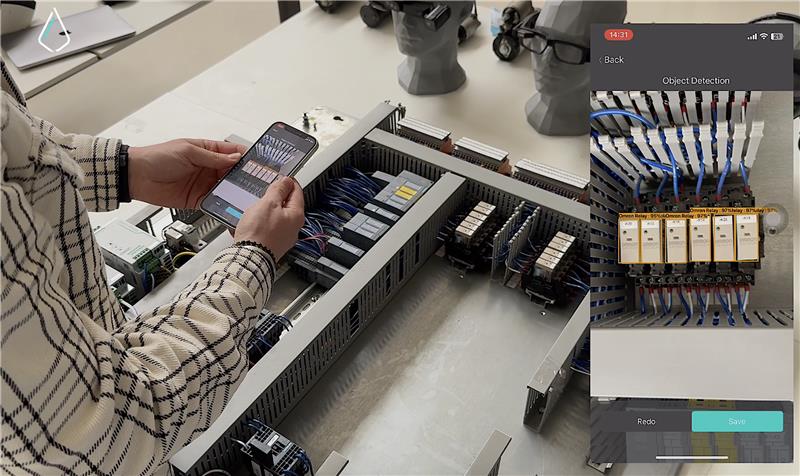
Introduction
The present wave of manufacturing is powered by connectivity. Digital manufacturing is key to that connectivity. Companies are increasingly turning to digital manufacturing to save time and money while streamlining production. Digital manufacturing uses computer systems to integrate data from various manufacturing processes. It relies on digital technologies such as 3D modeling, simulations, and analytics to improve production, supply chains, and other areas associated with manufacturing. The goal is to become more agile, save money, and respond to market conditions. Digital manufacturing is especially applicable to designing products, creating smart factories, and optimizing the value chain.
Companies can turn to digital models instead of physical processes. Here are three clear benefits of digital manufacturing:
1. Streamlines the product life cycle
Engineers can use digital manufacturing software to create a digital twin, which is essentially a virtual prototype or replica, instead of using materials such as foam or metal to create a physical one. They can then study the digital twin to determine how real-world conditions would affect proposed design changes and, in turn, discover potential flaws.
For example, a digital representation of a car engine may show that specific components will wear out faster than others. Technicians can study their digital twins to find solutions to those issues.
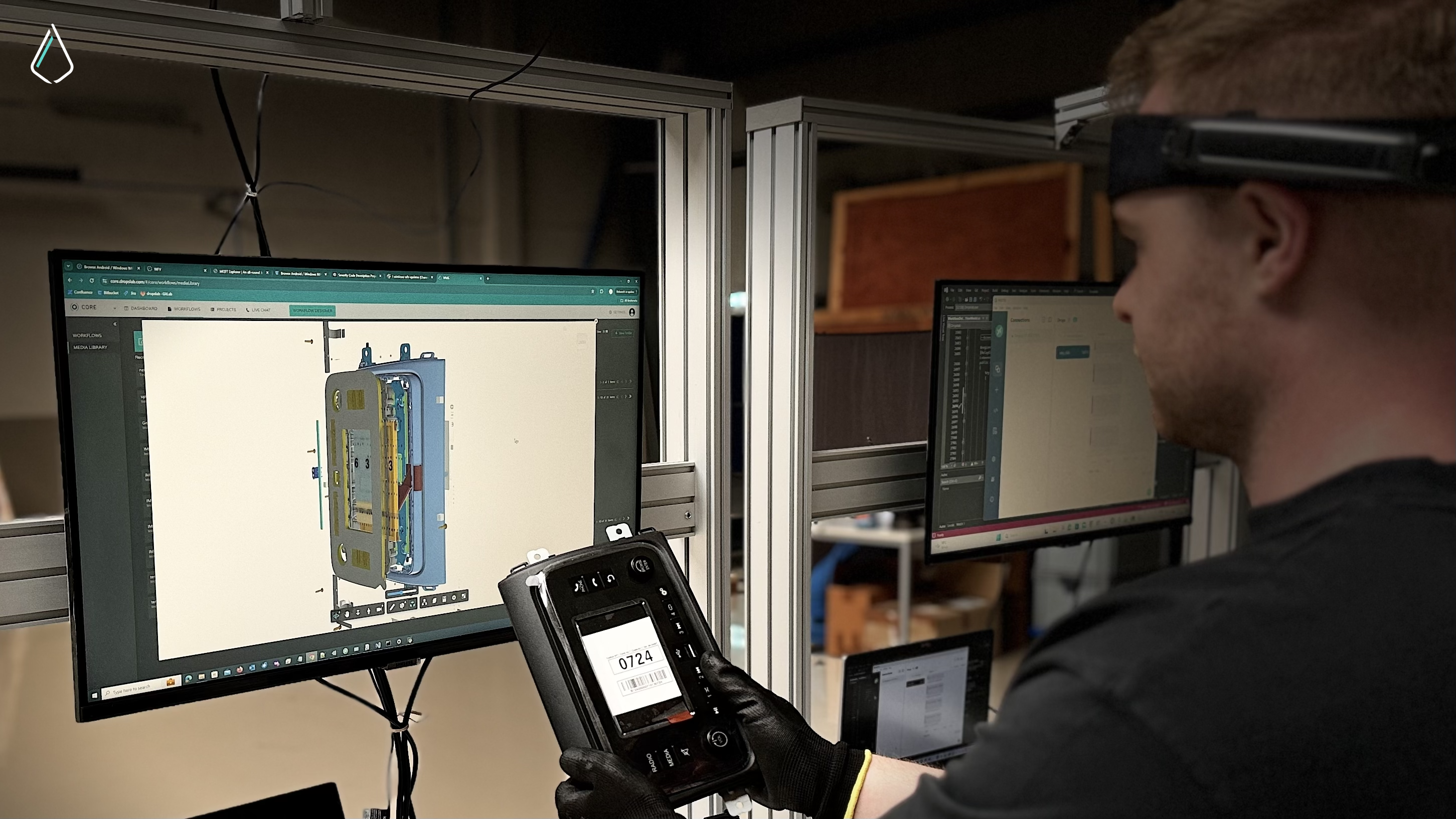

2. Helps optimize the value chain
Improving the value chain can be complicated. Digital manufacturing, with its focus on data and integration, can help with analysis all along the chain. It also enables experimentation via digital means, so there’s less physical and financial risk.
One way this plays out is in optimizing factory design. Companies can use digital manufacturing software to create virtual representations of factory floor layouts and simulate production processes. Technicians can discover potential bottlenecks and causes of waste or downtime before the factory is built, ensuring that it will run efficiently once it’s operational. Technicians can also use digital representations to experiment with different production methods without spending money on infrastructure or retooling.
For example, a factory manager may hear that a different kind of machine is more efficient than what is currently in use. Technicians can create a digital representation of the factory and swap out the old machines for new ones. The technicians can then study the simulation to see how the new machine will affect production. They may discover that a new machine is too costly, dangerous, or slow without spending money, endangering workers, or altering the production schedule.
3. Enables smart factories
Digital manufacturing provides the framework for smart factories closely associated with Industry 4.0. Although still in their infancy, smart factories use artificial intelligence, robotics, analytics, big data, and IoT to work largely autonomously. They are capable of self-correcting and alerting human workers when a problem occurs. Because smart factories are designed to run with minimal human interaction, one potential benefit is that people are freed from tedious, repetitive tasks and can focus on more interesting and important work.
Fully realized smart factories will be linked to other facilities in a digital network that supports supply chain management, monitors different facilities’ activities and needs, and enables multiple facilities to communicate and collaborate. These facilities will also be integrated across all departments and even with suppliers and customers, reducing the risk of error or duplication and increasing the chance that the appropriate person will catch and correct any mistakes that do occur.
For more on such topics, stay tuned to updates from Dropslab, here on the website and LinkedIn.
FAQs
1. What is digital manufacturing?
Essentially, digital manufacturing uses digital technologies like 3D modeling and analytics to optimize manufacturing processes, improving efficiency and agility.
2. How does digital manufacturing support smart factories?
It integrates AI, robotics, and IoT to enable autonomous factories that self-correct and communicate across facilities.
3. What are the key benefits of digital manufacturing?
It streamlines product development, optimizes production, and supports smart, automated factories.