Introduction
Maintenance is a critical aspect of any organization, ensuring that equipment, assets, and infrastructure function optimally. A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) plays a pivotal role in streamlining these maintenance operations. From work order management to asset tracking, CMMS solutions bring efficiency, accountability, and data-driven insights into maintenance processes. This article provides an in-depth overview of CMMS, its features, benefits, and applications while exploring how companies like Dropslab Technologies enhance these systems for modern businesses.
What is a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS)?
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a software platform designed to manage and optimize maintenance activities. CMMS solutions store detailed information about an organization’s assets, equipment, and maintenance schedules in a centralized database. By automating routine tasks, tracking performance metrics, and providing actionable insights, CMMS ensures that maintenance teams can proactively address issues before they escalate.
Key functionalities of Computerized Maintenance Management System include:
- Work Order Management: Organizing, prioritizing, and assigning maintenance tasks.
- Asset Management: Monitoring the lifecycle of equipment and infrastructure.
- Preventive Maintenance: Scheduling routine inspections to prevent unplanned downtime.
- Inventory Management: Tracking spare parts and ensuring sufficient stock levels.
- Reporting and Analytics: Providing insights into maintenance performance, costs, and trends.
By digitizing these processes, Computerized Maintenance Management System reduces manual effort and human errors, enabling organizations to achieve better operational efficiency and cost savings.
Key Features of a CMMS
A robust CMMS offers several features to support efficient maintenance management. These include centralized data management for storing information such as equipment details and vendor contacts, work order creation and tracking to organize tasks, and preventive maintenance scheduling to avoid unplanned downtime. Other features include asset management for lifecycle tracking, inventory management to maintain optimal stock levels, real-time monitoring integrated with IoT, and customizable reporting dashboards for actionable insights. These features collectively enhance transparency, operational efficiency, and data-driven decision-making.
Benefits of Implementing a CMMS
Organizations across industries reap significant rewards from adopting CMMS solutions. Below are some of the key benefits explained in detail:
1. Enhancing Efficiency and Reliability
CMMS streamlines maintenance workflows by automating routine tasks, reducing administrative burdens, and centralizing all critical data in one platform. By improving asset reliability through scheduled maintenance, organizations can minimize unexpected breakdowns and extend the lifespan of critical equipment. This results in improved productivity and operational stability.
2. Achieving Cost Savings
Preventive maintenance facilitated by Computerized Maintenance Management System reduces the need for costly emergency repairs and minimizes operational downtime. Furthermore, the system optimizes inventory management, eliminating overstocking or shortages, and ensuring that necessary parts are available precisely when needed. This optimization contributes to significant cost efficiency over time.
3. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Detailed record-keeping and automated reminders make it easier to adhere to industry-specific regulations. CMMS systems track inspection logs, maintenance history, and certification records, safeguarding organizations from penalties and enhancing audit preparedness.
4. Facilitating Informed Decisions
By providing comprehensive analytics and customizable reports, CMMS enables maintenance managers to make data-driven decisions regarding resource allocation, budgeting, and long-term asset planning. These insights allow for continuous process improvement, better forecasting, and strategic planning.
Applications of CMMS Across Industries
1. Manufacturing
Manufacturers use Computerized Maintenance Management System to monitor machinery, schedule maintenance, and optimize spare part inventories. By ensuring the availability and reliability of production equipment, CMMS minimizes downtime and enhances safety standards in manufacturing facilities.
2. Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare facilities rely on Computerized Maintenance Management System to manage medical equipment, ensure timely maintenance, and comply with regulatory standards. These systems play a crucial role in maintaining patient safety and delivering quality care.
3. Facilities Management
Facility managers utilize CMMS to maintain HVAC systems, lighting, and plumbing. By enabling preventive maintenance and quick resolution of issues, the system enhances energy efficiency and reduces maintenance costs while maintaining a comfortable environment for occupants.
4. Transportation and Logistics
CMMS supports fleet maintenance by scheduling vehicle servicing, tracking performance, and ensuring regulatory compliance. This increases safety, reliability, and efficiency across logistics operations, reducing delays and breakdowns.
5. Energy and Utilities
Energy providers leverage CMMS to monitor equipment in power plants and renewable energy installations. Predictive maintenance features help reduce downtime and optimize the performance of critical infrastructure.

Key Benefits of CMMS Solutions
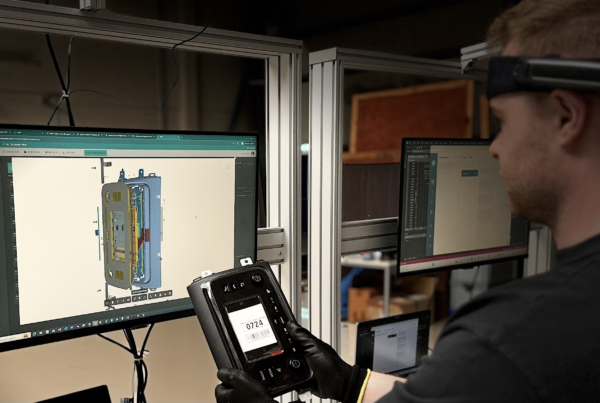
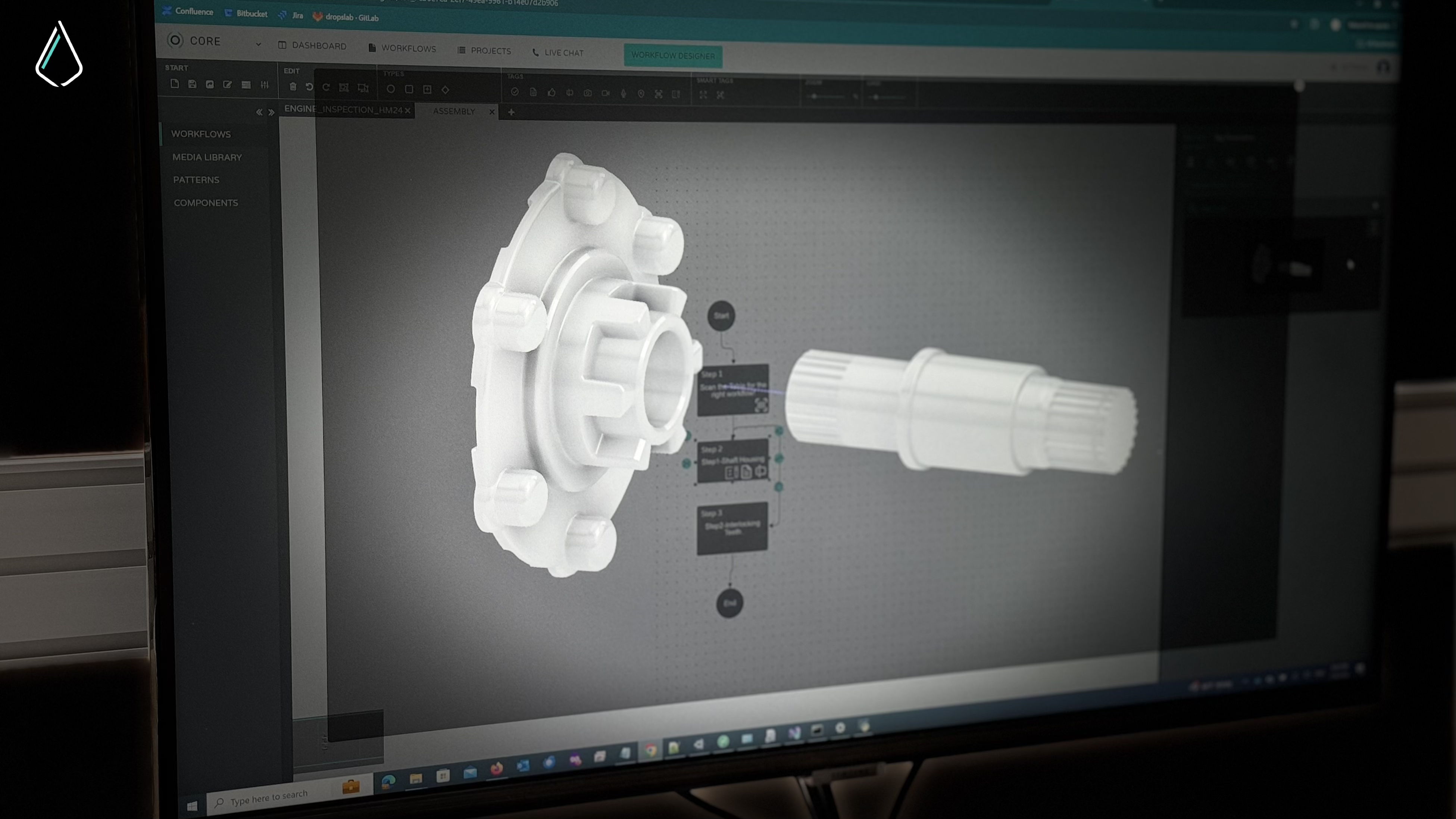
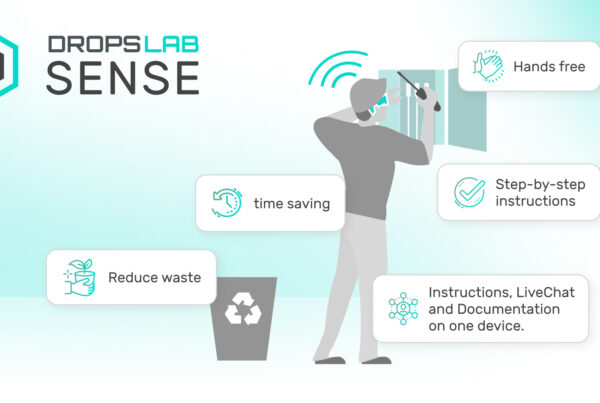
- AR-Enhanced Maintenance Technicians can use AR devices to view step-by-step maintenance instructions, improving task execution and safety.
- Real-Time Data Integration CMMS platforms connect seamlessly with IoT sensors, providing real-time insights into equipment conditions and enabling prompt action.
- Dynamic Workflows AI-driven analytics help optimize maintenance schedules and allocate resources efficiently, adapting to changing operational conditions.
- User-Friendly Interface It offers intuitive platforms that reduce the learning curve, ensuring quick adoption and better utilization by maintenance teams.
- Scalability for All Businesses From startups to large enterprises, CMMS scale according to business needs, providing flexible and future-proof maintenance management.
Conclusion
A Computerized Maintenance Management System is a vital tool for optimizing maintenance operations, reducing costs, and enhancing asset reliability. Across industries, CMMS solutions are transforming how organizations maintain equipment and infrastructure. Dropslab Technologies exemplifies innovation in this field, offering user-friendly, scalable platforms powered by AR and AI. Embracing CMMS is not just a step toward improved efficiency but a foundation for sustainable success and growth.
1. What are the core functionalities of a CMMS?
A CMMS typically includes work order management, asset management, preventive maintenance scheduling, inventory management, and reporting and analytics. These functionalities streamline maintenance operations, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
2. How does a CMMS enhance preventive maintenance?
By automating maintenance schedules and providing timely reminders, a CMMS ensures routine inspections are performed on time, reducing unplanned downtime and extending equipment lifespan.
3. What industries benefit most from CMMS solutions?
CMMS is widely used in manufacturing, healthcare, facilities management, transportation, logistics, and energy sectors. Its adaptability makes it valuable for any industry requiring organized maintenance processes.