Introduction
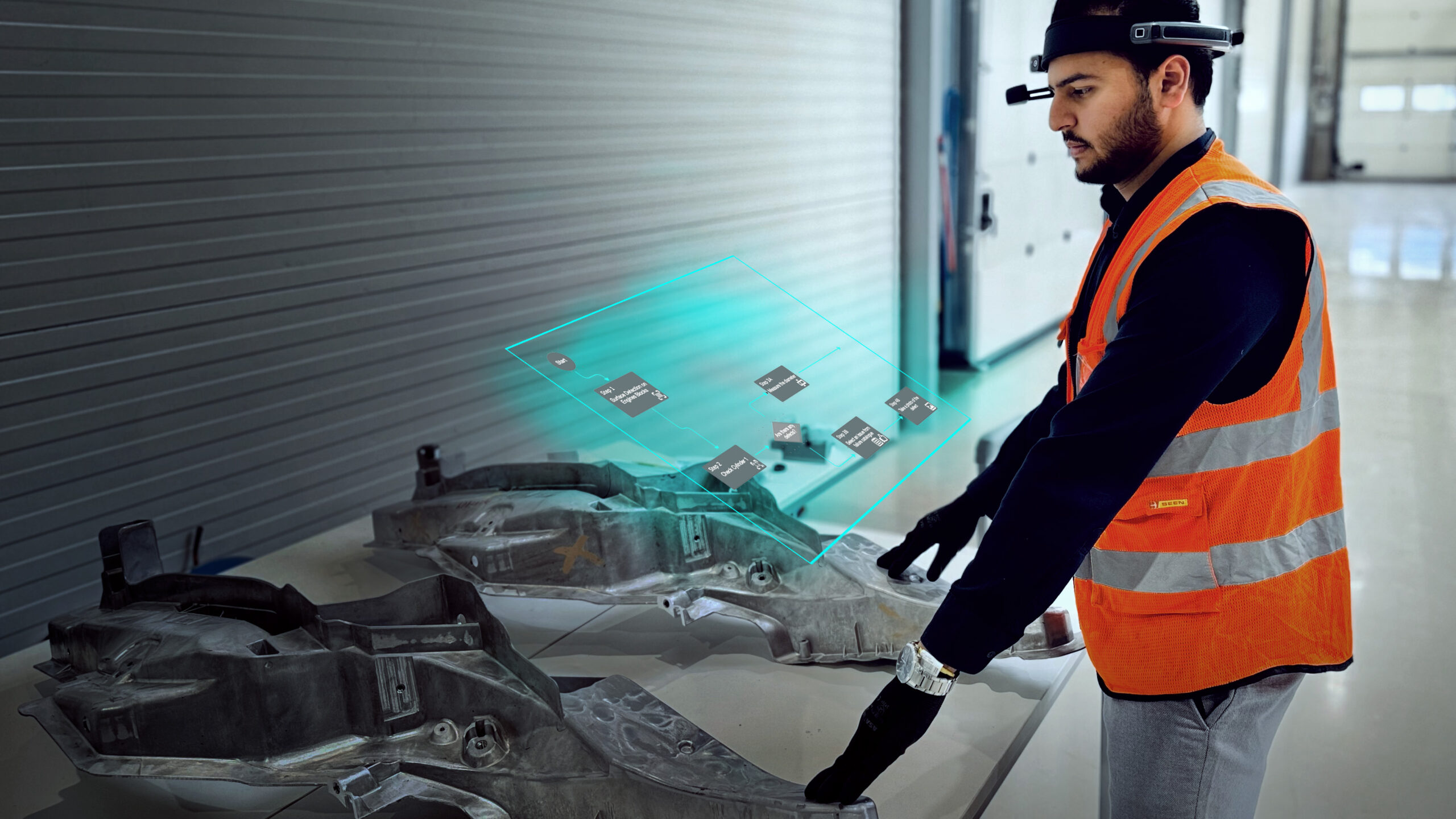
There are many wonders of Augmented Reality, and the phrase itself brings curiosity to tech and innovation enthusiasts globally. And, like everything, it is not safe from its own challenges. We at Dropslab have been passionate about AR integration to task executions for the longest time. In this blog, we explore some of the hidden challenges of AR, and how it can be solved.
Integration of AR in Manufacturing
The first augmented reality technology was developed in 1968 by Ivan Sutherland. However, it evolved over the years and now is dominating major industries. To name a few, the list includes automotive, healthcare, transportation, construction, and more. Along with the domination augmented reality has also developed and it now uses devices like AR glasses and smart screens to overlay digital information including data, images, videos, instructions, etc. onto the physical world. But before we move further in detail about augmented reality, we need to understand the difference between augmented reality and virtual reality, as given below.
| Aspect | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
| Environment | Enhances the real world with digital overlays. | Fully immersive in a virtual world. |
| Devices | AR glasses, smartphones, and tablets. | VR headsets like Oculus Rift, and HTC Vive. |
| Interaction | Combines physical and digital elements. | Interaction occurs only in the virtual space. |
| Applications | Manufacturing, training, healthcare. | Gaming, simulations, virtual tours. |
| Cost | Moderate to high. | High, due to advanced hardware. |
Key Disadvantages of Augmented Reality in Manufacturing
Augmented reality helps improve the manufacturing industries by providing benefits like real-time troubleshooting, simplified training, and optimised product development. However, regardless of these advantages, the disadvantages cannot be ignored which include:
1. High Initial Costs
The most common hurdles in adopting augmented reality in manufacturing are the high costs of initially implementing the systems. Possible investment costs can include acquiring augmented reality devices, incorporating the software with existing systems, and training staff. Moreover, regular maintenance, updates, and likely upgrades increase the costs over time. Since small manufacturing enterprises have limited budgets, these expenses can be excessive for them, possibly delaying the adoption of augmented reality technologies.
2. Complexity of Integration
Manufacturing industries generally rely on a combination of traditional systems and modern technologies and including augmented reality in this mix can be quite challenging. This will need customised solutions so the systems can be incorporated easily and are compatible with each other. Therefore, implementing these systems in the existing systems can usually take a lot of time and requires experts in the field. However, if the integration does not go as planned, then the investment costs can go to waste.
3. Learning Curve for Employees
While augmented reality simplifies the workflows in the long run, it also requires a lot of learning. Usually, employees are familiar with traditional methods and might find this shift to augmented reality a bit difficult. Thus, effective training programs are imperative to overcome this challenge but it might also require additional costs and can disrupt recurring operations temporarily.
4. Dependence on Reliable Connectivity
To work optimally, augmented reality applications usually require cloud connectivity and real-time data sharing. The shopfloors of manufacturing industries usually have limited internet access or the network infrastructure is unreliable which creates issues in the performance of augmented reality devices. However, due to these manufacturers can experience delays or inefficiencies during crucial operations.
5. Risk of Technology Overload
Manufacturers might face challenges in ensuring that augmented reality systems support and simplify their workflows rather than complicating them. Overloading operators with excessive digital information or instructions can result in confusion and decreased productivity. A balanced approach is imperative, where augmented reality systems are designed to provide only the most relevant data to avoid overwhelming frontline workers.
6. Maintenance and Downtime
Augmented reality hardware, such as smart glasses, requires regular maintenance so that it can function properly. However, device malfunctions or software bugs can lead to unexpected downtime, which can disrupt the complete manufacturing cycle. Also, as augmented reality technology is growing increasingly, manufacturers might need to update or replace their devices frequently, which can incur additional costs and delays.
Solving AR-driven issues with Dropslab
Dropslab Technologies believes that acknowledging and resolving the challenges of augmented reality in manufacturing is important as it can help in successful implementation and can also enable the industry to perform better. However, there are various ways to solve this issue, for example:
- Custom Solutions: Dropslab creates augmented reality applications that are customised to individual manufacturing environments. This ensures the integration with existing systems.
- Training Programs: By providing complete demos and training modules, Dropslab enables employees to adapt to AR technology quickly and efficiently.
- User-Centric Design: Dropslab emphasises intuitive and ergonomic augmented reality designs so that they can improve the user experience and keep them safe from information overload.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality holds immense potential for transforming manufacturing operations. While the technology offers numerous benefits, manufacturers must carefully weigh its disadvantages before implementing AR solutions. Challenges like high costs, complex integration, and the need for reliable connectivity are significant but not insurmountable. By collaborating with industry experts like Dropslab Technologies, manufacturers can effectively address these challenges and unlock AR’s potential as a key enabler of innovation and efficiency. AR, when implemented thoughtfully, can propel manufacturers toward a more agile, resilient, and competitive future.
FAQs
1. What are the main disadvantages of augmented reality in manufacturing?
The primary disadvantages include high implementation costs, complex system integration, a steep learning curve for employees, dependence on reliable connectivity, and potential device maintenance challenges.
2. How can manufacturers address the high cost of AR implementation?
Manufacturers can start with pilot projects to assess ROI before scaling up. Partnering with companies like Dropslab Technologies, which offers tailored AR solutions, can also help reduce unnecessary costs and ensure better value.
3. Does AR require continuous internet connectivity?
While many AR applications depend on real-time data sharing and cloud services, some solutions can function offline to an extent. Reliable connectivity, however, remains critical for optimal performance.