Introduction
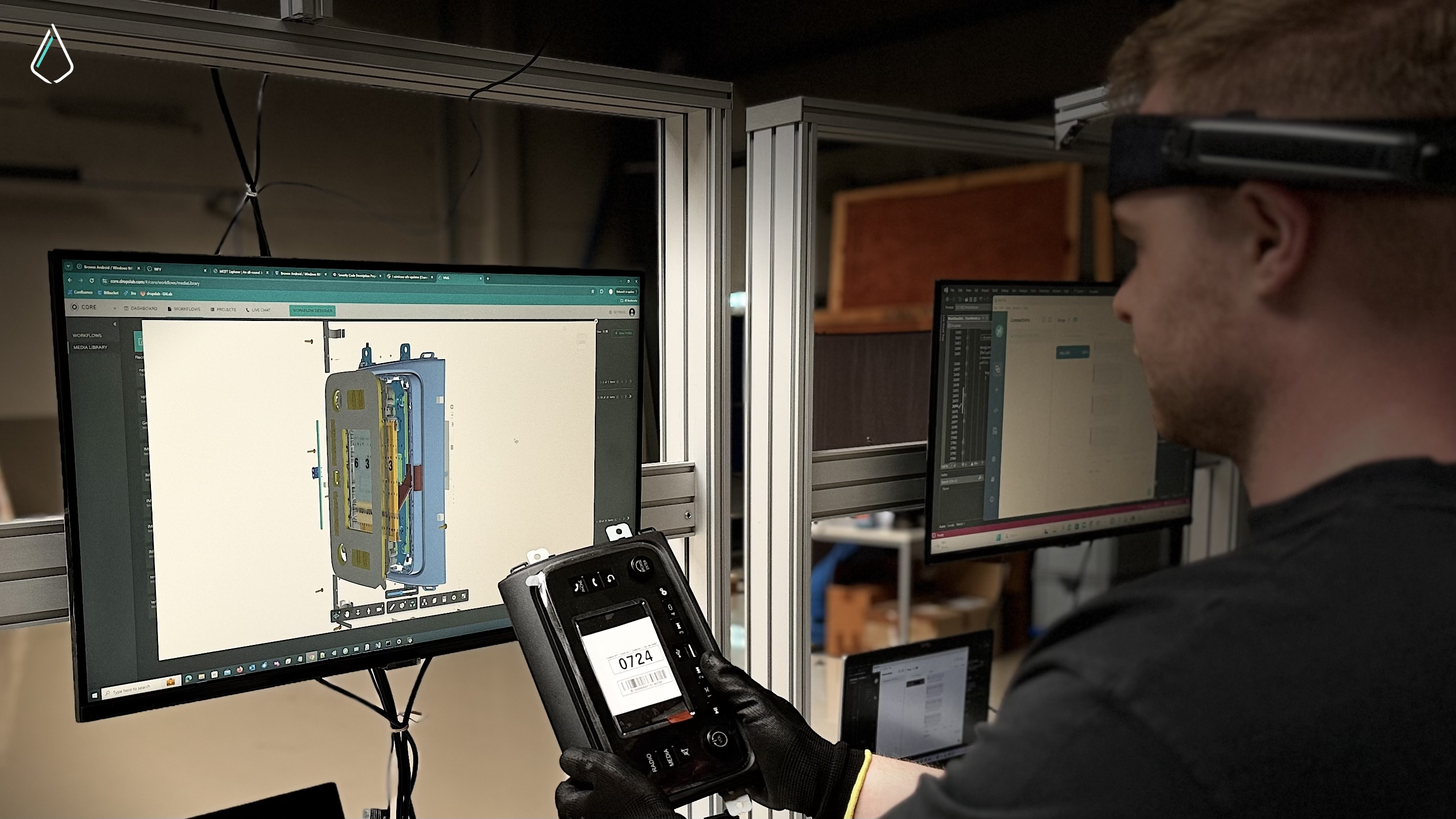
Warehousing is also considered a vital component of the supply chain because it makes sure that the movement of goods from sellers to buyers. However, the exponential growth of online retail as well as the need for more precise and quicker order processing has rendered traditional warehousing practices obsolete. This is where smart warehousing comes in. It is a contemporary method that employs the use of automation, robotics, data mining, and artificial intelligence for greater efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings.
Moving from traditional manual storage to automated smart warehouses has transformed the logistics industry. It permits businesses to operate more effectively and reduces errors while also meeting customer demands. This article analyzes the process of change in smart warehousing, the underlying technology that has enabled its expansion, and its implications on trade and consumer behavior.
The Shift from Traditional to Smart Warehousing
Today’s warehouses look nothing like what they used to look like. In the old days, these establishments worked on manual processes such as managing the inventory, picking orders and even processing the shipments. As these processes had a lot of human interaction, numerous errors were bound to happen leading to delays and backlogs during peak seasons.
The process of digital warehousing started in the late 1900s with the introduction of barcode scanning and warehouse management systems. The problem of tracking inventory was significantly alleviated as these new systems considerably simplified operations. When the new-age retailers Amazon and Alibaba emerged, they redefined the benchmarks of timely deliveries, thus forcing warehouses to embrace new forms of technology, if they wanted to remain competitive.
Now, automation has taken over the achingly cumbersome manual processes, so IoT, Cloud Computing, AI, and Robotics can all be employed to create data-driven storage facilities. There is a measurable increase in the rate of efficiency, precision, and speed of the operations undertaken.
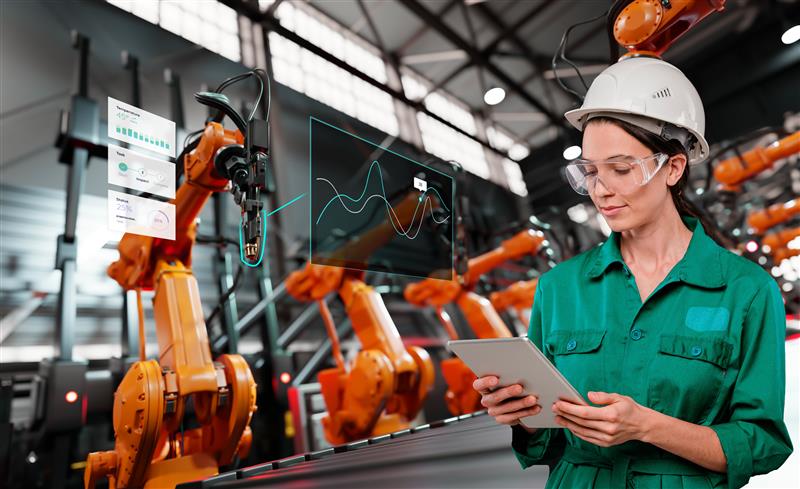

Key Technologies Powering Smart Warehousing
1. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
These systems ease the storage and recovery of products without the need for human intervention, using resources like automated cranes, conveyor systems, and shuttle lifts instead. They have many key advantages which consist of:
- Increasing storage density by using vertical space efficiently.
- Reducing labor costs and human errors in inventory handling.
- Improving order fulfillment speed with automated recovery.
These systems are especially helpful for industries that manage large inventory volumes, like e-commerce, pharmaceuticals, and retail.
2. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
This innovative technology is transforming how materials are delivered and managed in the warehouse. The AGV systems are pre-programmed to travel along specific routes using magnetic strips, laser guidance, or QR codes for tracking goods movement within different zones of the warehouse. Conversely, supply chain goods movement is managed by AMR systems, which use artificial intelligence and machine learning to reposition the items. They change the routes of the products in real-time in response to changing conditions in the warehouse and keep the workflow on schedule.
3. Automated Sortation Systems
These SBS eliminate the challenges associated with product identification and destination classification by automatically sorting and sending products to specific areas in the warehouse with minimal human effort. Different technologies such as bar codes, RFIDs, and optical sensors are used to accurately sort and steer products onto the right conveyor systems. Achieving these goals with the introduction of the sorting systems enables businesses to:
- By ensuring products are sent to the correct picking station, these systems improve order accuracy.
- By shifting to these systems, industries can reduce overall order fulfillment time and complete processes faster.
- These systems enable employees to concentrate on quality control rather than manual sorting which increases labor efficiency.
4. AI-Powered Predictive Analytics and Demand Estimating
AI-powered predictive analytics is changing the way industries manage their inventory, enabling them to:
- Anticipate demand trends and arrange their stock levels accordingly.
- Cut down on overstocking and stockouts, avoiding lost sales and the costs linked with increased inventory.
- Boost the flexibility of their supply chains, making sure warehouses are always stocked with the right products.
Companies like Amazon and Walmart, all depend on AI-powered predictive analysis to simplify their warehouse operations, minimize waste, and improve the efficiency of order fulfillment.
5. The Internet of Things (IoT) and Real-Time Tracking
IoT sensors are embedded in warehouse equipment, shelves, and even products to provide real-time tracking and monitoring. IoT technology enables:
- Live inventory updates, reducing discrepancies.
- Temperature and condition monitoring for sensitive goods.
- Faster problem resolution by identifying issues before they escalate.
- IoT integration allows warehouse managers to monitor operations remotely, improving transparency and decision-making.
Benefits of Smart Warehousing
The adoption of smart warehousing technologies provides several key advantages for businesses and consumers alike:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation streamlines operations, decreasing dependence on manual labor and decreasing human error.
- Improved Accuracy: AI-powered tracking and predictive analytics enhance order accuracy and inventory management.
- Optimized Space Utilization: High-density storage solutions maximize warehouse capacity, reducing costs.
- Faster Order Fulfillment: Robotic pickers and sortation systems accelerate the picking and packing process.
- Reduced Operational Costs: While initial investment costs are high, long-term savings on labor and errors outweigh expenses.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Smart warehouses adapt to fluctuations in demand, making them ideal for businesses of all sizes.
Conclusion
The evolution of smart warehousing is reshaping the logistics industry by integrating automation, robotics, AI, and IoT to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. Businesses that adopt these advanced technologies gain a competitive edge by improving order fulfillment speed, reducing operational costs, and optimizing inventory management. As technology continues to evolve, smart warehousing will become the standard for supply chain operations, ensuring faster deliveries, increased efficiency, and better customer satisfaction. Companies that embrace these innovations today will be the leaders of tomorrow’s logistics landscape.
FAQs
Q1: How does smart warehousing improve order accuracy?
Smart warehousing minimizes human errors by using barcode scanners, AI-driven picking systems, and automated sorting to ensure that products are correctly identified and dispatched.
Q2: Are smart warehouses only for large corporations?
No, small and mid-sized businesses can also implement scalable smart warehouse solutions, such as cloud-based inventory management and semi-automated picking systems.
Q3: What is the biggest challenge of transitioning to a smart warehouse?
The primary challenge is the high initial investment in automation and technology. However, businesses recover costs through improved efficiency, accuracy, and reduced labor expenses over time.
Q4: Do smart warehouses eliminate the need for human workers?
No, human workers remain essential for system oversight, quality control, and handling exceptions that automated systems cannot manage.