Introduction
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) is a group of techniques used to evaluate the properties, performance, and integrity of materials, components, or systems without causing damage. Unlike destructive testing, which requires dismantling or permanently altering the tested items, NDT ensures the equipment remains operational after the inspection. It is a cornerstone of quality control and preventive maintenance across industries, providing insights into structural health, detecting flaws, and averting potential failures.
Importance of Non-Destructive Testing
NDT plays a pivotal role in various industries, including aerospace, construction, manufacturing, and healthcare. By identifying defects such as cracks, corrosion, or misalignments early, NDT prevents costly downtime, ensures worker safety, and maintains compliance with industry standards. For instance, medical applications like X-rays and MRIs are prime examples of NDT, offering diagnostic insights without invasive procedures. Similarly, industrial NDT methods provide critical assessments without halting production or dismantling machinery.
Common Non-Destructive Testing Methods
Over the years, technological advancements have refined Non-Destructive Testing techniques to cater to diverse industrial needs. Below are some of the most widely used methods:
- Visual Testing (VT): Visual inspection is the simplest and most accessible form of NDT. Technicians examine assets to detect surface-level defects like cracks, corrosion, or deformation using tools like magnifying glasses, remote cameras, or drones. VT is often the first line of defence in routine maintenance.
- Vibration Analysis: This method involves using accelerometers and velocity sensors to measure an asset’s vibrations. Abnormal vibration patterns can signal issues like imbalances, misalignments, or mechanical wear. Technicians analyze these patterns to predict failures and schedule timely repairs.
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Ultrasonic testing employs high-frequency sound waves to evaluate material properties. A transducer sends sound waves into the material; defects reflect these waves, which are then analyzed using 3D visualization.
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT): This method involves applying a penetrant liquid over a material’s surface. The liquid seeps into surface defects like cracks or pores. After removing excess liquid, a developer is applied to draw the penetrant to the surface, revealing flaws.
- Radiographic Testing (RT): Using X-rays or gamma rays, RT detects internal flaws within materials. The radiation passes through the object and is captured on a detector, revealing defects such as voids or inclusions. Techniques like Computed Tomography (CT) and Digital Radiography (DR) enhance the imaging process.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT): MPT is used for ferromagnetic materials. A magnetic field is applied to the test object, and magnetic particles are sprinkled on its surface. The particles cluster around defects, making them visible under proper lighting conditions.
- Eddy Current Testing (ECT): ECT uses electromagnetic fields to detect surface and near-surface flaws in conductive materials. A coil induces eddy currents in the test object, and variations in these currents indicate defects.
- Leak Testing: Leak testing identifies leaks in pipelines and containers. Techniques range from simple bubble tests, where leaks produce visible bubbles, to advanced methods like pressure change analysis and mass spectrometry.
- Acoustic Emission Testing (AET): AET detects stress-induced acoustic waves emitted by materials under load. Sensors placed on the material surface capture these emissions, identifying areas of weakness or active crack growth.
Dropslab Technologies: Transforming NDT Practices
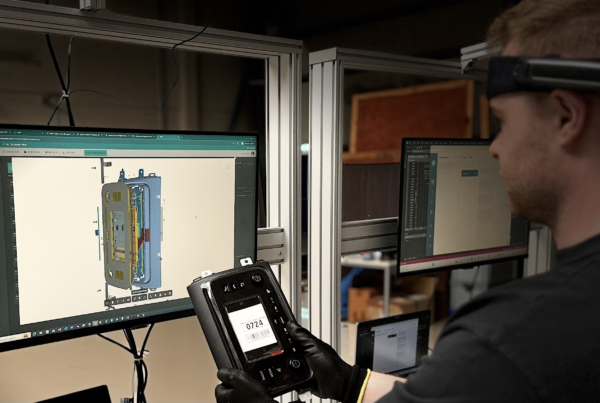
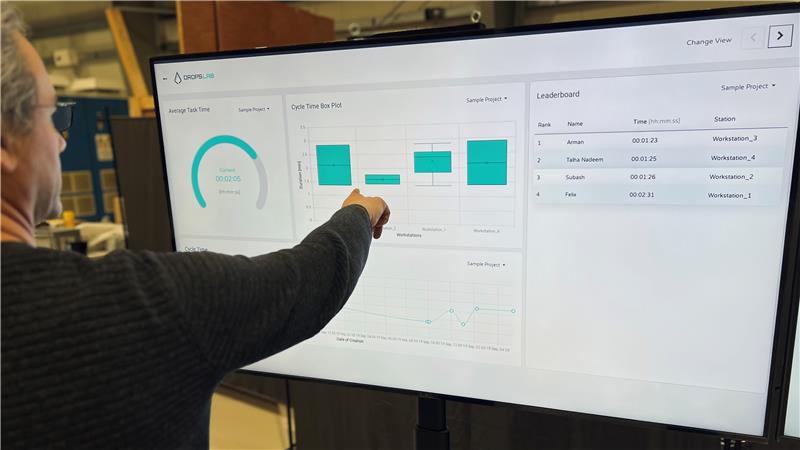
Dropslab Technologies is at the forefront of innovation in non-destructive testing. By integrating cutting-edge tools and technologies, Dropslab provides comprehensive Non-Destructive Testing solutions tailored to diverse industrial needs. Their advanced software and hardware platforms enable precise data collection, real-time analysis, and actionable insights, significantly improving the reliability of inspection processes. Industries ranging from aerospace to manufacturing rely on Dropslab’s expertise to enhance safety, optimize maintenance schedules, and minimize operational disruptions.
With Dropslab’s solutions, clients gain access to automated systems, AI-driven diagnostics, and cloud-based platforms for storing and analyzing inspection data. These innovations empower maintenance teams to identify defects with greater accuracy and efficiency, ensuring that their assets remain in peak condition.
ISO 19.100 and Industry Standards
Non-destructive testing adheres to stringent standards outlined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) under ISO 19.100. This standard provides comprehensive guidelines on testing methods, equipment specifications, and compliance protocols. Following these standards ensures reliable and consistent test results, fostering industry-wide confidence in NDT practices.
Application Across Industries
- Aerospace: Aircraft components are subjected to NDT to detect cracks, corrosion, and material fatigue. Techniques like ultrasonic testing and eddy current testing are particularly effective in maintaining structural integrity.
- Construction: NDT methods like radiography and ultrasonic testing are crucial in assessing weld quality, concrete integrity, and structural health in buildings and bridges.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, NDT ensures product quality by detecting material inconsistencies, voids, or defects in castings and welds.
- Healthcare: Medical imaging techniques, such as X-rays and MRIs, are non-invasive NDT methods that revolutionize diagnostics.
- Oil and Gas: Pipelines, storage tanks, and drilling equipment undergo NDT to prevent leaks and catastrophic failures.
Future of Non-Destructive Testing
As industries adopt smarter technologies, NDT is evolving to integrate automation, real-time data analytics, and AI-driven diagnostics. Ultrasonic testing, in particular, is gaining traction due to its precision and adaptability. Time-of-Flight Diffraction (ToFD) and Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT) are emerging as preferred techniques for complex applications.
Benefits of NDT
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) offers numerous benefits that make it indispensable across various industries. It is a cost-effective method for identifying defects early, significantly reducing repair costs and preventing operational downtime. Non-Destructive Testing also enhances workplace safety by detecting potential hazards before they pose a risk to personnel or equipment.
Additionally, it is an environmentally friendly approach, as it minimizes waste by avoiding the destruction of materials during testing processes. The versatility of NDT allows it to be applied to a wide range of materials and industries, from manufacturing to aerospace. Furthermore, it is a highly reliable technique, providing accurate and repeatable results that ensure consistent quality and safety in critical applications.
Conclusion
Non-Destructive Testing is an indispensable tool in modern industries, offering a blend of efficiency, safety, and precision. By adopting advanced NDT methods, organizations can ensure the longevity and reliability of their assets. Dropslab Technologies stands as a beacon of innovation, providing state-of-the-art solutions that empower industries to stay ahead in the competitive landscape. As technology continues to evolve, Dropslab remains committed to driving advancements in Non-Destructive Testing, paving the way for smarter and more sustainable inspection practices.
FAQs
1. What is Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)?
NDT refers to testing methods used to evaluate materials, components, or systems without causing damage. It ensures operational integrity and is widely used in industries like aerospace, construction, and manufacturing.
2. How does Ultrasonic Testing work?
Ultrasonic Testing uses high-frequency sound waves to detect flaws in materials. A transducer sends sound waves through the material and reflected waves from defects are analyzed to locate and assess the flaw.
3. Why is Non-Destructive Testing important in preventive maintenance?
Non-Destructive Testing identifies defects before they lead to failures, ensuring equipment reliability, reducing downtime, and enhancing safety.
4. What are some commonly used Non-Destructive Testing methods?
Popular Non-Destructive Testing methods include Visual Testing, Ultrasonic Testing, Liquid Penetrant Testing, Radiographic Testing, Magnetic Particle Testing, and Acoustic Emission Testing.
5. How is technology shaping the future of Non-Destructive Testing?
Advancements in automation, AI, and real-time analytics enhance NDT’s precision and efficiency. Techniques like Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing are gaining popularity for their detailed diagnostics. By leveraging advanced Non-Destructive Testing techniques, industries can ensure operational excellence, safety, and compliance, driving progress and sustainability in their respective fields.