Introduction
Manufacturing sector is constantly in a flux. Meeting demands require not only producing the goods, but sourcing the raw materials, managing the rising cost and mitigating unpredicted delays. In such situations what becomes the savior is a system that increases efficiency, decreases downtime and helps navigate the rising industrial costs. One such reliable system is Smart Manufacturing.
Hence, in this article, we will be discussing the five main pillars of smart manufacturing which are helping industries to become better and more efficient:
1. IT and OT Integration
One of the main aspects of smart manufacturing is the combination of information technology and operational technology. By merging these two technologies which give us data and network systems, and factory machinery and control systems, respectively, industries can create new environments where data flows without any issue between systems and machines. The integration of both technologies in the industrial sector brings with them some benefits which include:
- Real-time monitoring and control of operations in the manufacturing industry.
- Improved decision-making through data-driven insights.
- Enhanced cybersecurity measures for industrial systems.
- Reduced downtime through predictive maintenance.
The merging of information and operational technology helps in achieving improved overall efficiency, decreased operational costs, and enhanced system performance.
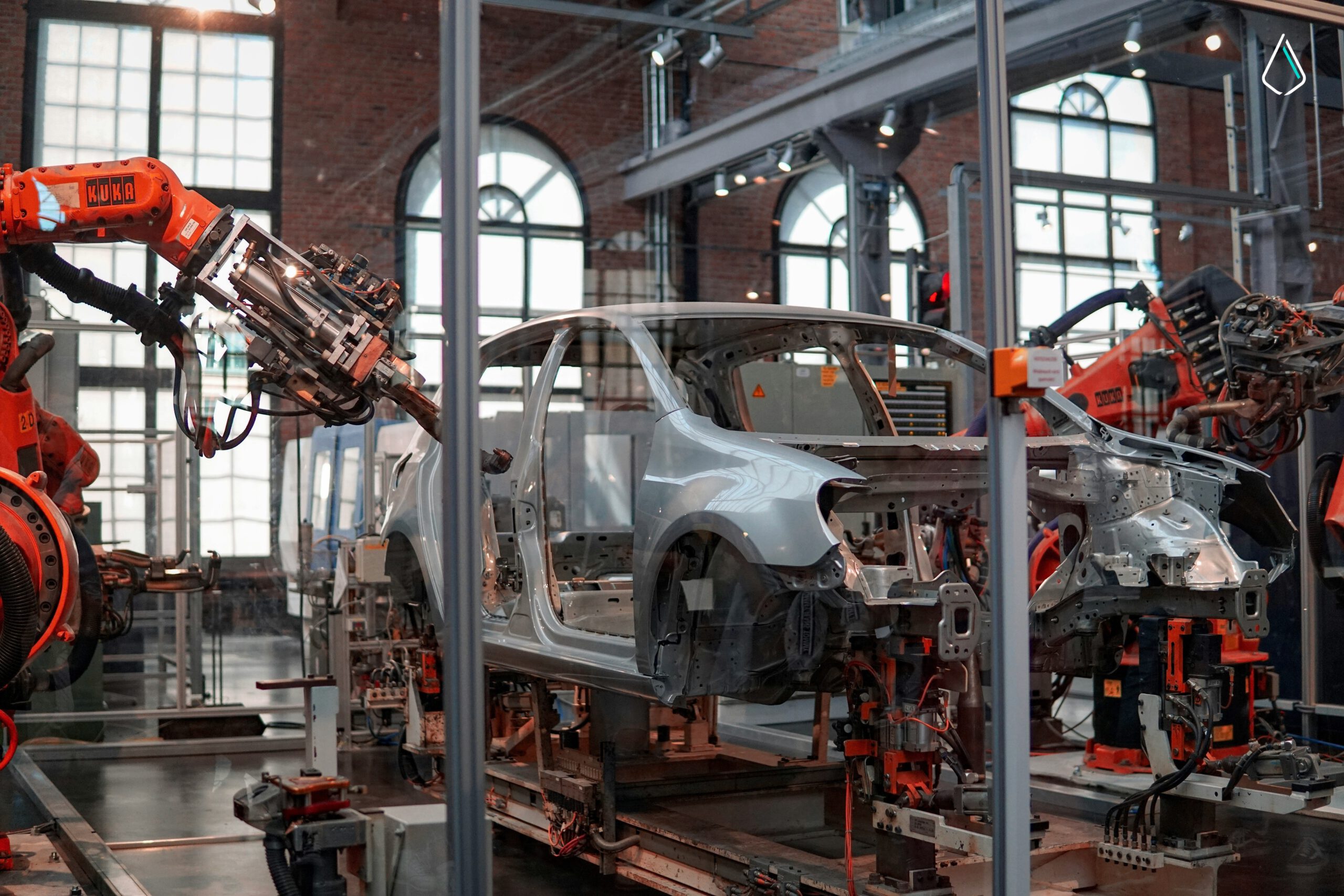
2. Automation and Robotics
Automation and Robotics are one of the pillars of smart manufacturing as they change the way things are being manufactured within industries. The use of this technology in the manufacturing process helps remove monotonic work and errors created by humans. It also improves operational accuracy and quality control within the manufacturing supply chain. Automation and Robotics have various examples such as:
- Assembly line automation for faster and more consistent production.
- Robotic arms for precision tasks such as welding and packaging.
- Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) for material handling.
- AI-driven automation for adaptive and intelligent manufacturing.
An automated system allows a manufacturer to carry out more activities than before, which in turn increases the level of safety within the workplace, lowers the overall cost of labor, and preserves the desired quality.

3. Data Analytics
Smart manufacturing, along with its analytics capabilities, allows for predictive maintenance, operation optimization, and knowledge-based real-time decision-making. Through the utilization of big data analytics, manufacturers are provided useful information such as production performance, opportunities, or difficulties that may arise.
Key Applications of Data Analytics
- It helps in predictive maintenance as it analyzes machine data to predict and prevent failures.
- Offers process optimization by identifying inefficiencies and optimizing production workflows.
- Improves quality control using data to detect defects and enhance product quality.
- Improves logistics and inventory management through data-driven insights.
These advanced data analytics help improve operational productivity while decreasing waste and maximizing profitability.
4. Digital Twin and Cyber-Physical Systems
The digital twin is a digital depiction of a real-world asset, system, or operation that facilitates real-time monitoring, simulation, and optimization. Cyber-physical systems (CPS) provide a linking mechanism among the physical and digital environments through the use of sensors, data processing, and automated control.
Advantages of Digital Twin and CPS
- Real-time simulation and scenario analysis for decision-making.
- Enhanced predictive maintenance and equipment lifespan optimization.
- Improved production planning and resource allocation.
- Reduced operational risks through virtual testing.
The use of digital twins and CPS allows manufacturers to operate more efficiently, minimize costs, and foster a more flexible and adaptive production environment.
5. Cloud Computing and IoT
Cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) allow data to be processed in real time from any place around the globe. These technologies enable remote monitoring, automation, and interconnectivity from various manufacturing sites.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing and IoT
- Scalability: Businesses can expand operations without significant infrastructure investments.
- Remote Access: Enables manufacturers to monitor and control processes from anywhere.
- Data Security: Advanced encryption and security protocols protect sensitive manufacturing data.
- Enhanced Connectivity: IoT devices enable seamless communication between machines, sensors, and control systems.
These technologies allow manufacturers to enhance efficiency and streamline operations giving them an advantage in the competitive global market.
Conclusion
Smart manufacturing is transforming the industrial sector by integrating advanced technologies that enhance efficiency, productivity, and flexibility. The key pillars of IT and OT integration, automation and robotics, data analytics, digital twin and cyber-physical systems, and cloud computing with IoT work together to create a highly connected and intelligent manufacturing ecosystem. By embracing these technologies, businesses can stay ahead in the competitive market, optimize operations, and ensure long-term sustainability. Whether large enterprises or SMEs, manufacturers that adopt smart manufacturing will reap significant benefits in terms of cost savings, quality improvement, and operational efficiency.
FAQs
1. What are the main challenges of implementing smart manufacturing?
The main challenges include high initial investment costs, integration complexity, cybersecurity risks, and workforce upskilling requirements. However, the long-term benefits outweigh these challenges, making smart manufacturing a worthwhile investment.
2. How does predictive maintenance improve manufacturing operations?
Data analytics and machine learning are used in predictive maintenance to anticipate machine breakdowns before they occur. This results in more efficient operations by lowering maintenance costs, increasing equipment longevity, and decreasing downtime.
3. Can SMEs adopt smart manufacturing?
Yes, SMEs can adopt smart manufacturing by implementing scalable solutions such as cloud-based software, IoT devices, and automation tools. Many affordable options allow SMEs to gradually transition into smart manufacturing without large upfront investments.